December is only just beginning, and yet it feels like everyone around us is getting sick. If you share the same observation, chances are it isn’t just your imagination making things up. Flu season is officially underway, and it looks like it’s hit the US early and hit particularly hard. Federal and state officials have been warning the public about a potential “twindemic” occurring at the onset of the flu season following two unusually quiet ones that coincided with the two-year global rampage of the Sars-Cov-2 virus. But as Covid restrictions have all but disappeared, a host of viruses suppressed by masking, quarantine, social distancing, and vaccination are all coming back with a vengeance. The twin threats of the novel coronavirus and influenza are at the forefront of this viral attack.
However, why are federal and state health officials so worried about this particular flu season? The flu is and always has been a potentially lethal viral illness. Nevertheless, plenty of other factors contribute to a flu season. It gets so bad that it can cause strain in the healthcare system and economic disruptions. It will decrease the quality of life for most American families and individuals. How these scenarios will play out will ultimately depend on how the public responds to the mitigation efforts led by the government and the health sector. Meanwhile, here are the things you need to know about why this flu and cold season could be worse than any we’ve seen in a while.
What’s so bad about the flu?
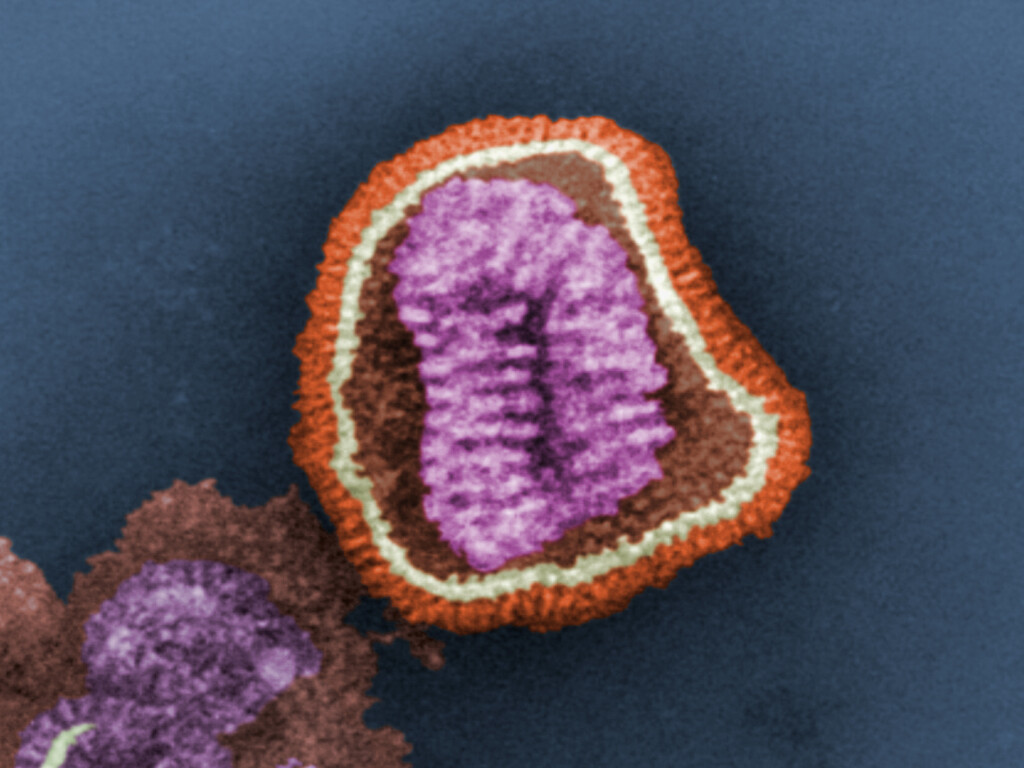
Also known as influenza, the flu is a respiratory illness caused by a virus, which is a microscopic infectious agent that invades your cells and makes you sick. It is highly contagious, spreading from one person to another through respiratory droplets or by touching contaminated surfaces and bringing hands to face. Because of this mode of transmission, flu prevention measures include mask-wearing and keeping a distance of about 6 feet from people suspected of having the flu. Typically, adults can spread the virus from the day before symptoms show up to seven days after and are most contagious within the first three to four days of experiencing symptoms.
The fact that the flu has become commonplace by no means makes it less lethal, nor should it be brushed off as a minor concern. Health officials’ campaign for widespread public uptake of flu vaccines each season for a reason – the flu virus spreads easily. Once you catch it, it can be deadly, whether you are healthy or not, especially for people with risk factors. Inoculation is the only thing sure to prevent the worst effects of the flu virus. In the past, new flu strains have caused deadly pandemics that racked up deaths in the millions. The only reason we enjoy greater protection from it today is that advances in health sciences allow researchers to study the virus’ evolution closely and stay one step ahead of new strains through the development of vaccines.
