Many dread encountering a serious medical situation, but chances are you’ll encounter some kind of emergency in your life. Being prepared will help reduce the element of the unknown and may even save a life-possibly your own. Many illnesses and injuries can threaten lives, from heart attacks to snake bites to drowning and more. Often knowledge is key to reacting appropriately to these scenarios.
Here’s a list, in no particular order, of medical knowledge that could save a life. This isn’t meant to be exhaustive or replace formal medical training, but rather as a jumping-off point to help you be more prepared for the medical emergencies you may encounter in your life. Medical knowledge of some key conditions can help treat minor injuries, know when it’s time to see a doctor.
Education on critical symptoms and first aid classes are the best routes to ensuring you’re prepared for any situation. While many of these situations are stressful and terrifying, being prepared helps you stay calm when it’s most needed. But always remember to call emergency services in cases of life-threatening illness or injury.
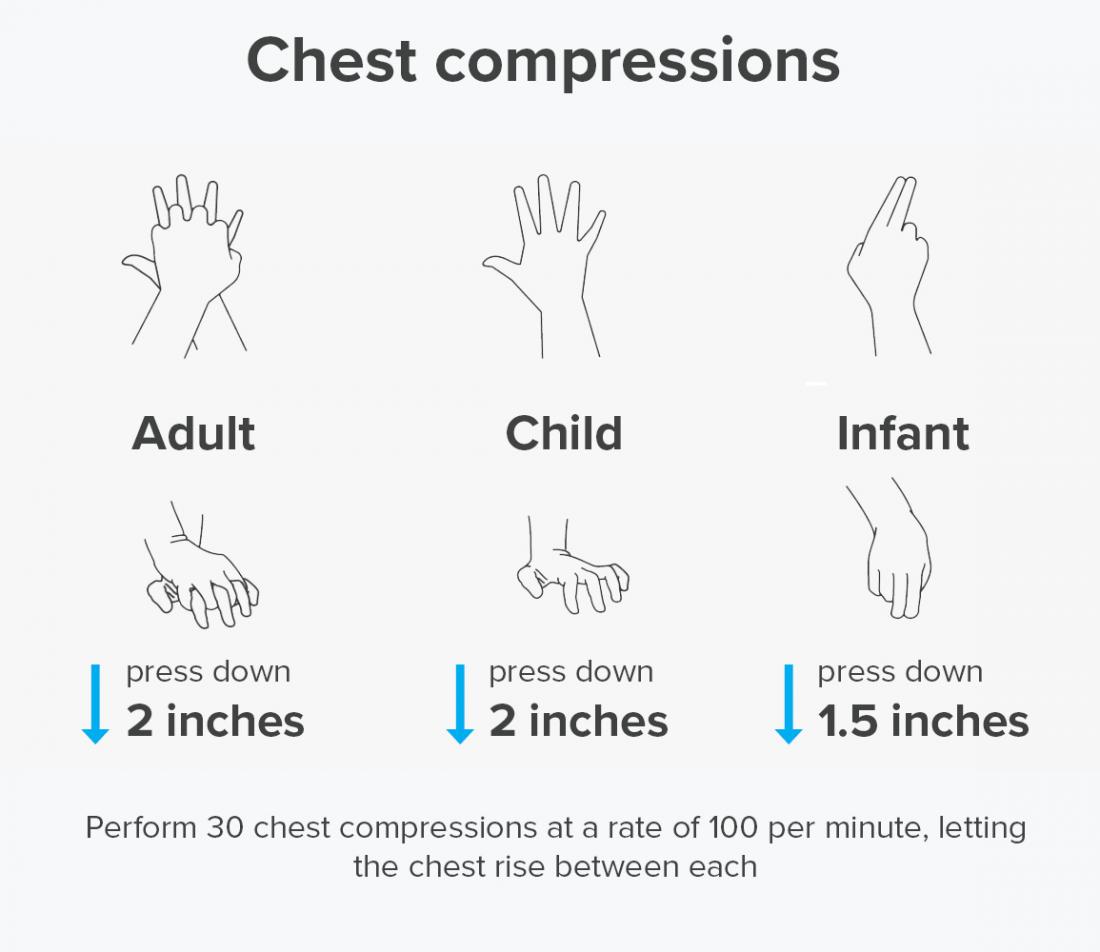
Chest Compressions
When someone becomes unresponsive-that is, they’re unconscious and not showing signs of breathing or a pulse-chest compressions become critical. Chest compressions are part of a process known as cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR as it’s often known, used to revive someone close to death. Taking a class is the best way to be prepared for situations requiring chest compressions since it’s important to use the correct technique, which varies between adults, children, and infants. This may enable you to keep someone alive until emergency services arrive.
